Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Vehicle Ownership Documents

Vehicle ownership documents are an essential part of any car transaction, serving as the legal proof of who owns the vehicle. Issued by state authorities, often through the DMV, these documents detail important information about the car and its owner.
A standard title includes the vehicle’s unique VIN, make, model, year, and sometimes lienholder information if the car is financed. Each state has its own format and security features for titles, which help protect against fraud.
When buying or selling a car, ensuring the authenticity of the title is critical. Any discrepancies or missing information on the title can lead to complications during the ownership transfer. Buyers should carefully review the title for accurate details and verify that it matches the vehicle in question.
For instance, the VIN listed on the title must correspond to the VIN located on the car itself. Additionally, sellers should confirm they have the right to transfer ownership and that there are no unresolved liens or legal issues tied to the vehicle.
Some states may issue electronic titles instead of physical documents, which streamline the process but still carry the same legal weight. Regardless of format, having a legitimate title is a non-negotiable requirement for a smooth car transaction.
The Process of Car Sale Paperwork
- Car sale paperwork involves several key steps to ensure a smooth transfer of ownership between the buyer and seller. The process typically begins with drafting a bill of sale, which serves as a record of the transaction. This document includes details such as the vehicle’s make, model, year, VIN, sale price, and the names and signatures of both parties. It’s a crucial part of the sale that provides proof of the agreed terms.
- Another essential component is the title transfer, where the seller signs the vehicle title to release ownership to the buyer. Some states require this step to be notarized, depending on local regulations. Along with the title, the seller must provide an odometer disclosure, which is mandated under federal law to confirm the vehicle’s mileage at the time of sale. This prevents fraudulent practices, such as rolling back the odometer to mislead buyers.
- To finalize the sale, buyers must register the vehicle under their name and secure insurance. State DMVs typically require the completed title and any additional paperwork, such as a lien release if the vehicle was previously financed. Fees for registration and taxes are also part of this process, which varies depending on state laws.
- In private sales, it’s essential that both parties understand their responsibilities. The seller must ensure all documents are completed accurately, while the buyer should verify the paperwork before submitting it to the DMV. When purchasing from a dealership, some of these steps may be handled on behalf of the buyer, simplifying the process. However, it’s still essential to review all documents for accuracy and ensure compliance with state regulations.
Reasons for Using Fake Car Titles
- Counterfeit car titles are sometimes used to mislead buyers or obscure a vehicle’s true history. Financial motives are a primary driver, as fraudulent sellers may use fake titles to sell vehicles obtained through theft or other illegal means. These titles create the illusion of legitimate ownership, allowing the seller to profit from a car they don’t have the right to sell.
- In other cases, fake titles are used to hide issues that would otherwise deter buyers. Sellers might attempt to cover up significant damage from accidents, unresolved liens, or a salvage history. By altering or forging a title, they can misrepresent the car’s value and condition, deceiving buyers into paying more than the vehicle is worth.
- Another tactic, known as title washing, involves creating a fraudulent title to remove salvage or rebuilt branding, which indicates that the car has been previously written off due to severe damage. This process enables sellers to market the vehicle as having a clean title, bypassing the stigma and reduced value associated with a branded title.
How to Identify a Fake Car Title
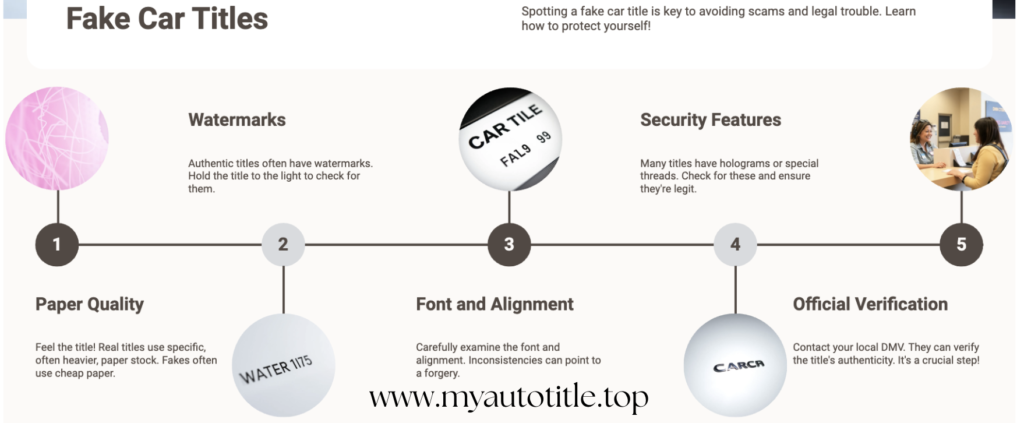
Detecting a fake vehicle title involves paying close attention to specific details and security features. Start by examining the document for physical inconsistencies. Genuine titles often include watermarks, raised seals, or other tamper-proof features that are difficult to replicate.
If these elements are missing or appear altered, the document may be counterfeit. Additionally, check for inconsistencies in the text, such as unusual fonts, misaligned printing, or incorrect information.
Always verify the information on the title matches the vehicle itself. This includes comparing the VIN on the title to the VIN physically displayed on the car. Any discrepancies, no matter how minor, should raise concerns. Other vehicle details, like the make, model, and year, should also align with what’s being sold.
Review the ownership history on the title, if provided. A clean and consistent history is a good sign, but gaps or irregularities might indicate tampering. Pay special attention to whether the vehicle has a salvage or rebuilt branding, as some sellers might attempt to erase this information with a fake title.
To further verify the title’s legitimacy, reach out to the issuing authority, typically the DMV. Many states offer services that allow you to confirm the title’s status or obtain a vehicle history report. These reports can provide valuable insight into the car’s background and reveal issues that aren’t immediately visible on the title.
If you’re still uncertain, professional services like Carfax or AutoCheck can be used to access detailed vehicle history reports. These reports often highlight discrepancies between the title and the car’s actual history, such as unreported accidents or branding inconsistencies.
Taking the time to inspect these details and cross-reference the information ensures that you have a clear understanding of the vehicle’s history and legal status before moving forward with a purchase.
Legal Consequences of Using or Selling a Car with a Fake Title
Engaging in the use or sale of fake car titles is a serious legal matter that can lead to criminal charges, including fraud, forgery, and theft. State laws vary, but penalties often include substantial fines, imprisonment, and restitution payments to victims. These actions undermine trust in the vehicle market and disrupt legitimate ownership transfers, making them a priority for law enforcement and regulatory agencies.
Individuals involved in these schemes not only face criminal charges but may also encounter civil lawsuits. Buyers who unknowingly purchase a car with a fraudulent title can file claims to recover financial losses, often resulting in lengthy legal battles for the perpetrators. Additionally, tampering with vehicle documentation can result in the forfeiture of assets obtained through the fraudulent activity.
Authorities frequently investigate fake title cases due to their connection to broader illegal activities, such as car theft rings or insurance fraud. In such instances, those caught using or selling fake titles may also face additional charges related to these crimes. The severity of penalties often depends on the scale and intent behind the offense, with organized operations facing harsher consequences.
The ripple effects of title fraud extend beyond legal ramifications. Vehicles sold with fraudulent titles can be seized, leaving the buyer without compensation or recourse. Sellers found guilty of these crimes may also be banned from conducting future vehicle transactions or operating within the auto industry.
Tips for Protecting Yourself in Car Purchases
When purchasing a car, taking proactive steps can help you avoid potential pitfalls. Start by conducting thorough research on the vehicle you’re considering. Use the VIN to access a trusted vehicle history report, which can reveal details like prior accidents, title branding, and odometer discrepancies. Reviewing this information ensures you’re aware of any issues before making a decision.
Inspect the title closely for any signs of tampering or inconsistencies. Pay attention to physical elements, such as watermarks or seals, and confirm that the details on the title match the vehicle itself. Verify that the VIN, make, model, and year align with the car you’re purchasing. If anything appears off, take extra time to investigate further.
When dealing with private sellers, ask for documentation that supports their ownership, such as a bill of sale or lien release if applicable. Be cautious if a seller is unwilling to provide these documents or tries to rush the transaction. Trustworthy sellers are typically transparent and willing to answer questions.
Meeting in person to finalize the sale allows you to physically inspect the car and cross-check the paperwork. If you’re unsure about any aspect of the transaction, consider consulting a professional, such as a mechanic or an attorney, to evaluate the situation.
If buying from a dealership, confirm that they are properly licensed and reputable. Take time to carefully review the paperwork they provide and clarify any terms you don’t fully understand before signing.
Stay informed about state-specific requirements for vehicle transactions, as processes can vary. Some states may have unique rules for title transfers or registration, so it’s essential to follow local guidelines.
Lastly, trust your instincts. If something doesn’t feel right or the deal seems too good to be true, it’s worth pausing to investigate further. By staying vigilant and informed, you can reduce the likelihood of encountering fraudulent practices and ensure a smooth, secure car purchase.
Fake Vehicle Titles During Sales
Fake Vehicle Titles During Sales have become a significant concern in the automotive market, as fraudsters exploit unsuspecting buyers eager to acquire their next vehicle. These counterfeit documents often mimic genuine titles with alarming accuracy, making it increasingly difficult for consumers to discern authenticity at first glance.
Unscrupulous sellers may present fake titles that falsely claim ownership or omit critical information such as liens and odometer readings, thereby misleading potential buyers about the vehicle’s history and legal standing.
This shadowy practice not only jeopardizes individual transactions but also undermines trust within the entire marketplace, prompting law enforcement agencies and regulatory bodies to ramp up efforts against title fraud.
Buyers are advised to conduct thorough background checks on both the seller and the vehicle’s title by utilizing state resources or digital verification systems designed specifically for this purpose, ensuring they are not unwittingly entering into an illicit agreement that could result in financial loss or legal complications down the line.